Affiliate marketing and dropshipping are two of the most popular online business models for earning money without owning or managing inventory.
Both help you to build a profitable online business, but they work in different ways:
- Affiliate Marketing: Promote others’ products for a commission.
- Dropshipping: Sell your own products and keep the profit.
But which one should you choose?

Don’t worry, you don’t have to struggle like this man in the picture.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through a clear, side-by-side comparison of Affiliate Marketing vs Dropshipping. What they are, how they work, types of different models, and more.
And by the end of the article, you will know which mode suits your skill, budget, and goal.
So, let’s get started by learning the key comparison.
Quick Comparison: Affiliate Marketing vs Dropshipping
| Criteria | Affiliate Marketing | Dropshipping | Winner |
Business Model | Commission-based: You promote an existing merchant’s products via affiliate links and earn a commission per sale. | Profit-based: You run your own online store, source products, and forward orders to a supplier who ships on your behalf. | Depends on your preference |
Brand Ownership | You promote another company’s brand, but you have no control over their branding or customer relationships. | By building your own brand, you control the customer experience and create brand loyalty. | Dropshipping |
Control | Less control. The end company decides product quality, pricing, customer service, and commission rates. | Full control over branding, pricing, product quality, customer service, and store design. | Dropshipping |
Inventory | No need to source or manage inventory. | You don’t hold stock, but you must know SKUs and manage orders with your supplier. | Affiliate Marketing |
Payment | Most affiliate programs have a minimum payout threshold (both amount and time). So the payout can be delayed. | You receive payment from customers first, then pay the supplier, giving better cash flow. | Dropshipping |
Risk | Very low. If a product fails, you just stop promoting it. | Moderate, Supplier mistakes, refunds, or delivery delay fall on you. | Affiliate Marketing |
Startup cost | Very low. You just need a website, social account, or some ad spend. | It’s low, but higher than affiliate marketing due to the costs of store setup, apps, and ads. | Affiliate Marketing |
Scalability | Limited. Commissions stay fixed unless traffic scales massively. | High. You can add products, adjust pricing, and grow like a full store.. | Dropshipping |
Customer Service | Once someone clicks and buys, your job is done. | You are responsible for handling complaints, issuing refunds, and providing customer support. | Affiliate Marketing |
Profit Margin | Commissions range from 5–50%, usually $2–$1,000+ per sale. | Margins average 10–30%, but you control pricing and can improve them with branding. | Tie |
Skills Require | SEO, content creation, funnel building, paid ads. | Store setup, product research, paid ads, and operations. | Depends on your skill |
Flexibility | High – Create content once and keep earning passively. | Low – daily store, SKU, and customer management required. | Affiliate Marketing |
Startup Speed | Fast. Join an affiliate program and start promoting within days. | Slower – takes time to set up a whole store, source and test products. | Affiliate Marketing |
| Long-Term Potential | Great for a side hustle, but limited control means limited growth. | It can grow into a full brand and later hold stock if desired. | Dropshipping |
Detailed Overview: Affiliate Marketing
What is Affiliate Marketing?
Affiliate marketing is a way of earning money by promoting someone else’s products or services. You don’t need to create your own product, manage inventory, or deal with customer support.
Instead, your job is to use your marketing skills, like content creation, SEO, or paid ads, to get these products in front of potential buyers when they are searching for them.
When promoting these products, you have to share the unique affiliate links provided by the affiliate program.
If a customer clicks this link from your website, YouTube channel, or social media and makes a purchase from the store you have referred, you will earn an affiliate commission on that sale. As simple as that!
How Affiliate Marketing Works?
Here’s the simple overview of how affiliate marketing works:
Your content → Affiliate Link → Customer Click → Merchant Website → Purchase → Commission Earned
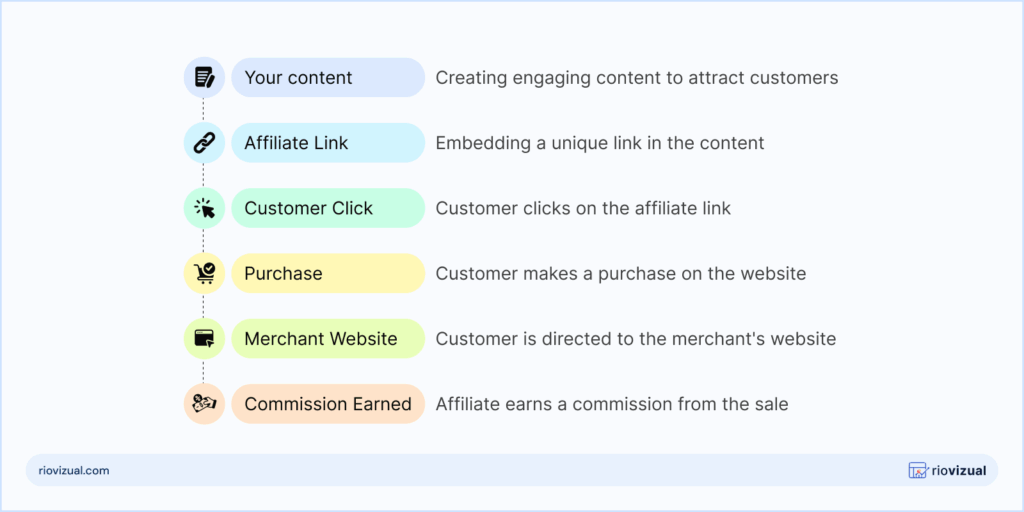
Sounds easy, right? But there’s more happening behind the scenes, where a tracking system ensures that each sale credited to you is made from your effort.
This is where the cookie policy comes into play. Not that cookie you love with tea!
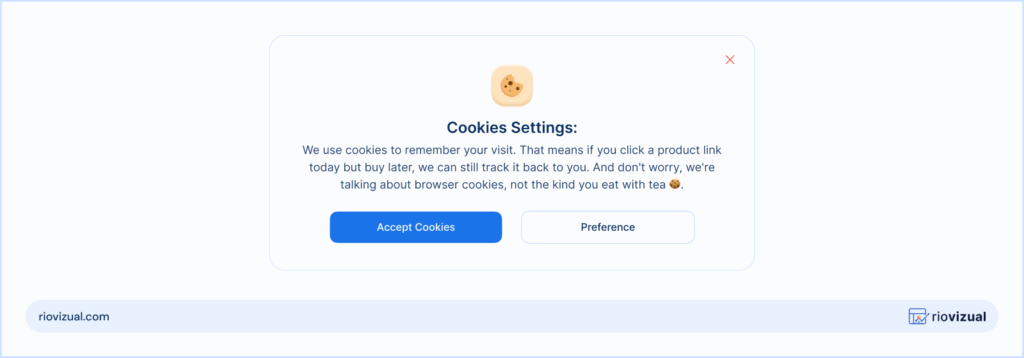
The cookie tracks the clicks your affiliate link gets. They remember if someone clicks your link but doesn’t buy immediately.
That means you can still earn commission if the same customer comes to the same merchant’s store and buys the product later within the cookie window.
And the good part is that most affiliate programs offer a cookie window of at least 14 to 180 days.
However, you can still lose commission if:
- Customers clear their browser cookies before making the purchase.
- They click on another affiliate link before making the purchase.
- Someone clicks on your link from one device and purchases from another.
Keep in mind that some programs also pay you for leads (like email signups or free trials). And some even pay for the amount of traffic they get.
And not all the affiliate programs follow the last-click attribution model. So, you can still earn commission as the first referral.
Types of Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing has different types based on the involvement and promotional activities. Understanding these types of affiliate marketing can help you determine the best approach that aligns with your skills and goals.
Understanding the different types of affiliate marketing can help you determine the best approach that aligns with your skills and goals.
1. Unattached Affiliate Marketing:
Unattached affiliate marketing is the simplest and quickest way to start an affiliate marketing business.
The term “Unattached” hints at this process, where you are not attached to the niche and do not need to build authority or build any audience.
Instead, you run paid ads to promote your affiliate links, such as Google Ads and Facebook Ads. And if someone clicks on these links, they will directly land on the merchant’s website.
2. Related Affiliate Marketing:
Related affiliate marketing is a type of affiliate marketing where you already have an audience base in a specific niche, and you have joined an affiliate program that fits with that niche.
And you recommend those products to your audience using your affiliate links without having used or experienced them firsthand.
For example:
- A tech blogger might recommend a new software tool they haven’t tried themselves but know is popular in their niche.
- A YouTube influencer could review a product using stock footage or infographics and add the affiliate purchase link in the video description.
Keep in mind that while this method works well because it leverages your niche authority, it can backfire if the product disappoints your audience.
3. Involved Affiliate Marketing:
Involved affiliate marketing is a type of affiliate marketing where you actively use and test the products you are promoting. You then share your genuine experiences with your audience.
This approach works great for building trust because your recommendations are based on firsthand usage rather than relying on secondhand information.
For example:
- A fitness blogger who uses a protein supplement or workout gear writes a detailed review on their blog, including results, photos, and proof of usage. They also provide a purchase link through their unique affiliate link.
- A YouTuber films him using the software, showing all the features step by step within the screen record, and then drops the affiliate link in the video description.
This is the most recommended type for building a long-term affiliate marketing business. Trust is the biggest factor in generating consistent income, and nothing builds it better than firsthand experience.
Pros and Cons Of Affiliate Marketing:
Like any other business model, affiliate marketing comes with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding both sides will help you decide whether it’s the right choice for you.
✅ Pros of Affiliate Marketing:
- Low Investment and Risk: You don’t need to create a product, manage stock, or rent a warehouse. Startup costs are minimal, where a website, YouTube channel, or even a social media profile is enough to get started.
- Easy to Start: Joining an affiliate program is very easy. You can join any affiliate program, get your unique affiliate link, and start promoting within a few days.
- Passive Income Potential: Create content once and keep earning commissions for months or even years, which gives affiliate marketing a strong passive income potential.
- Flexibility and Freedom: You can work from anywhere and set your own schedule. Running an affiliate business gives you more flexibility than traditional jobs.
- No Inventory, Shipping, and Customer Support: Once a customer clicks your link and buys from the merchant, your job is done. You don’t have to handle storage, shipping, or after-sales support.
- Diverse Opportunities: Thousands of affiliate programs exist across every niche. It brings diverse opportunities to find and promote multiple programs.
- Scalability: An Affiliate marketing business can scale with massive traffic growth. Later, you can expand your business by launching your own products and services, leveraging your existing audience.
- Global Reach: Affiliate marketing eliminates geographical boundaries and enables you to build a business and reach customers worldwide, no matter where you live.
❌ Cons of Affiliate Marketing:
- High Competition: Popular niches in affiliate marketing are very crowded and highly competitive. Standing out in these niches required a strong content strategy, SEO, and even paid advertising.
- Pay Only for Result: You will earn commissions only for the referrals that convert into sales (or action). No matter how much awareness you create or traffic you drive. You don’t get paid unless results happen.
- Fluctuating Income: Affiliate earnings fluctuate month to month, depending on traffic and conversion rates. This makes it harder to predict a consistent income, similar to other businesses.
- Limited Control on Brand and Customer Experience: You lack control over the branding, product quality, pricing, and customer support of the products you promote, as the merchant handles these aspects.
- Commission dependency: Your entire income relies on the commission structure. If a program reduces its rate, shuts down, or changes terms, your revenue can drop suddenly.
- Cash Flow Challenge: Most affiliate programs have a minimum payout threshold and a waiting period. This can create a cash flow challenge for the new affiliate businesses.
- Risk of Losing Commissions: You can still lose the commission after sales if the cookie expires, the customer switches devices, or if another affiliate link overwrites yours.
- Regulatory and Legal Concerns: Affiliate marketing businesses can be penalized by legal authorities, such as the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC), if they fail to disclose affiliate relationships and add clear labels to affiliate links, like “Affiliate Link” or “Sponsored” in buttons or CTAs.
- Algorithm Change: Unlike other websites, affiliate traffic can fluctuate due to sudden algorithm updates, such as Google’s SEO algorithm updates and other Social media algorithm updates affecting organic visibility.
Detailed Overview: Dropshipping:
What is Dropshipping?
Dropshipping is a way to run an online store where you sell products without keeping any inventory yourself. Instead, you act as a store in the front and a middleman between the customer and the supplier at the backend.
This is a powerful business model that allows you to create your own brand without manufacturing or stocking your own product.
Instead, when a customer places an order from your store, you forward that order to a supplier or manufacturer. The supplier then ships the product directly to the customer on your behalf.
That means you don’t have to worry about managing stock, packaging, or the delivery of the product. But you remain responsible for the overall customer experience, customer support, and after-sales services.
How Dropshipping Works?
Here is a simple overview of how Dropshipping works:
Customer order → Your online store → You forward the order to the supplier → The Supplier ships the product on your behalf → You keep the profit margin.
In the middle of this process, you keep the profit margin of $10. This is how a dropshipping business works.
Sounds simple, right? But just like affiliate marketing, there is more happening behind the scenes. In dropshipping, you are running a business where you need to take care of:
- Product research (finding quality products that actually sell)
- Store design and setup (Creating e-commerce website)
- Marketing (SEO, Ads, Social Media)
- Customer Service (handling refunds, complaints, and questions).
Types of Dropshipping:
Not all Dropshipping businesses are the same. There are different approaches depending on how you want to run the store.
Understanding these types will help you decide the best approach that matches your skills and goals.
Based on Sourcing Method:
There are 3 types of dropshipping based on the sourcing methods. Which are:
1. Traditional dropshipping (Wholesale):
This is the most common and widely used dropshipping model. In traditional dropshipping, you source products directly from wholesale suppliers, manufacturers, or large online marketplaces like AliExpress, DHgate, or Alibaba.
You then list these products in your online store with a markup to earn your profit margin.
The key idea here is simple: you don’t keep any stock. Instead, when a customer places an order in your store, you purchase the product from the wholesale supplier at a lower price, and the supplier ships it directly to your customer.
2. Domestic dropshipping:
A Dropshipping method is considered domestic if you partner with suppliers within your own country instead of sourcing internationally. And also, you target the local audience of your country.
The main benefit of this model is faster shipping times and better quality control, since suppliers are closer to your customers.
This approach is especially popular for niches where customers expect quick delivery (like food supplements, beauty products, or pet supplies).
Even though domestic products may cost more than international ones, the reliability and shorter delivery times make them attractive for building trust and repeat sales.
3. Hybrid dropshipping:
Hybrid dropshipping combines the best of both worlds. In this model, you stock your best-selling or high-demand products locally for faster delivery, while still dropshipping the rest from international suppliers.
This gives you more control over shipping speed and customer satisfaction, while also keeping your catalog wide with products you don’t want to stock yourself. Many growing stores use this approach to balance customer trust and business scalability.
Based on Product Type:
Based on the product type, dropshipping can be categorized into 3 types. Here are the main approaches:
1. Print-on-demand (POD):
Print-on-demand is a dropshipping model where products are created only after a customer places an order. This method is especially popular for custom-designed items such as t-shirts, mugs, hoodies, posters, or phone cases.
It allows you to sell creative, personalized products without holding any inventory or worrying about bulk production.
For example, an artist designs custom t-shirt graphics in multiple styles and colors. They upload the designs to their own online store or a marketplace. When a customer orders a design, the artist forwards the order to the supplier, who then prints it on the t-shirt and ships it directly to the customer.
2. Private label dropshipping:
Private label dropshipping involves sourcing generic products from a supplier and selling them under your own brand name.
The supplier manufactures the product, but you customize the packaging, labels, or logo so that it looks like your own unique brand.
This model helps you build your brand identity in the market, create customer loyalty, and stand out from competitors, even though the product itself comes from a third-party supplier.
For example, A skincare entrepreneur sources a generic serum from a supplier at $10, adds custom branding and packaging, and lists it on their store for $35.
When a customer orders, the entrepreneur forwards the order to the supplier, who ships it in the custom packaging under the entrepreneur’s brand.
3. White label dropshipping:
White label dropshipping involves selling generic products that carry your branding, even though the same products may also be available from other retailers under different labels.
Unlike private label products, which grant you exclusivity for your brand, white label products are widely accessible and customized with various brand names.
This business model enables you to establish a brand presence, but it provides less uniqueness because many competitors may offer the same product featuring their own labels.
For example, an online electronics store sources wireless earbuds from a supplier at $15. They add their brand name to the packaging and list them for $40. While they build some brand recognition, other stores can still sell the same earbuds with different branding.
Pros and Cons Of Dropshipping:
Just like affiliate marketing and any other business model, dropshipping also has its own pros and cons. Understanding both sides will help you decide whether it’s the right choice for you.
✅ Pros of Dropshipping:
- Low Startup Cost: You don’t need to purchase inventory upfront or rent a warehouse. All you need is an online store and a supplier to start.
- No Inventory Management: Suppliers handle storage, packaging, and shipping, so you don’t need to worry about managing stock.
- Wide Range of Products: You can list a large variety of products in your store without keeping them physically. This flexibility lets you test different niches easily.
- Brand Ownership: Unlike affiliate marketing, dropshipping allows you to build your own brand identity and gain more control over branding, product quality, and customer experience.
- Scalability: It’s easy to scale by adding new products, expanding into more niches, or automating order fulfillment. Growth doesn’t require handling more stock.
- Global Reach: With the right suppliers and audience, you can sell and ship products to customers worldwide, not just in your local market.
- Better Cash Flow: Customers pay you upfront. Then, you pay the supplier, allowing you to use customer funds to cover your costs and improve cash flow.
❌ Cons of Dropshipping:
- High Competition: Popular niches are crowded, making it hard to stand out without strong branding or marketing effort.
- Low Margins: Since many sellers compete on the same products, average profit margins are often only 10–30%.
- Moderate Risk: If suppliers make mistakes (delayed shipping, wrong or low-quality products), your store’s reputation takes the hit, and you are responsible for these.
- Less Control: You don’t control product quality, shipping speed, or supplier reliability. Customers often blame you for issues that are beyond your control.
- Inventory Issue: If a supplier runs out of stock, you may need to cancel or delay orders, which hurts customer trust.
- Building a Brand is Difficult: Selling generic products from suppliers makes it harder to create a unique brand identity, unless you move into private label dropshipping.
- Customer Service Challanges: As a store, you have to take the responsibility of customer service, including refunds, complaints, and returns, which can be challenging for low-margin products.
- Supplier Dependence: Your business depends heavily on the suppliers you choose. If they stop selling, change prices, or lower quality, your business suffers.
- Marketing Cost: Most dropshipping stores rely on paid ads (Google, Facebook, TikTok, etc) to drive traffic. Advertising costs can quickly eat into your profit margins.
Affiliate Marketing vs Dropshipping: Which one is best for you?
Now you understand how both models work, let’s break down the key factors that will help you decide which one fits your skills, goals, time, and resources.
1. Budget/startup cost:
- Affiliate Marketing: Very low. You only need a website, blog, or social media account to start. Most of the investment goes into creating content, while running ads is optional.
- Dropshipping: Remains low compared to traditional businesses, but it is higher than affiliate marketing. You’ll need to set up an online store, pay for apps, and usually spend on paid ads.
Our Recommendation: If budget is your primary concern, go with affiliate marketing.
2. Inventory Management:
- Affiliate Marketing: Zero inventory. You only promote links, and the merchant handles everything.
- Dropshipping: No physical stock required, but you still need to manage product listings, SKUs, and supplier coordination.
Our Recommendation: Affiliate marketing is simpler if you don’t want to manage these extra steps.
3. Risk-Taking Ability:
- Affiliate Marketing: Very low risk. If a product doesn’t perform, you just stop promoting it.
- Dropshipping: Moderate risk. Supplier errors, refunds, or shipping delays can directly affect your reputation, sales, and overall business.
Our Recommendation: If you prefer a no-risk side hustle, affiliate marketing is a safer option.
4. Scalability:
- Affiliate Marketing: Limited. Income grows mainly with traffic. Commission rates usually don’t increase unless you create your own products or services.
- Dropshipping: Highly scalable. You can add new products, raise prices, and expand into different niches as you grow.
Our Recommendation: For long-term growth potential, dropshipping has the edge.
5. Control Over Business:
- Affiliate Marketing: Minimal. You can’t control pricing, product quality, or customer experience since the merchant owns these aspects.
- Dropshipping: High. You control pricing, branding, product selection, and the overall customer journey.
Our Recommendation: If control matters to you, dropshipping is the better choice.
6. Customer Service:
- Affiliate Marketing: None. Once a customer clicks and buys, your job is done.
- Dropshipping: You’re responsible for handling customer complaints, refunds, and queries.
Our Recommendation: Choose affiliate marketing if you want to avoid customer service altogether.
7. Profit Margin:
- Affiliate Marketing: Commissions typically range from 5–50%, sometimes much higher with high-ticket programs.
- Dropshipping: Average profit margins are 10–30%, but since you set the prices, there’s potential to improve margins through branding or upsells.
Our Recommendation: For more control over pricing, consider dropshipping. If you prefer higher commissions without overhead, go with affiliate marketing (especially high-ticket programs).
8. Skills Required:
- Affiliate Marketing: SEO, content creation, social media marketing, funnel building, or running paid ads.
- Dropshipping: Store setup, product research, paid advertising, supplier management, and customer service.
Our Recommendation: Both require marketing skills. If you love creating content and growing organic traffic, choose affiliate marketing. If you enjoy media buying and running ads, dropshipping may suit you better.
9. Time Commitment:
- Affiliate Marketing: Lower. You can create evergreen content once and let it generate passive income over time.
- Dropshipping: Higher. You’ll need to handle daily operations, customer feedback, supplier communication, and ongoing product research.
Our Recommendation: Affiliate marketing is better if you want a side hustle with less daily involvement.
10. Long-Term Potential:
- Affiliate Marketing: Great for building side income, but limited control makes it harder to scale into a whole business.
- Dropshipping: Can evolve into a full-fledged brand. Over time, you can move into private label or even hold your own inventory.
Our Recommendation: For entrepreneurs looking to build a long-term business, dropshipping offers more substantial growth potential.
FAQ:
Conclusion
Affiliate Marketing and Dropshipping are both profitable and sustainable online business models. But depending on your skills, goals, and budget. We have tried to share all the key information with you. Now choose one based on your need.
Have you already decided which path to choose? If yes, please share your thoughts with a comment.



Leave a comment